Introduction
In today’s rapidly evolving manufacturing landscape, businesses must adopt smarter, data-driven approaches to remain competitive. A Manufacturing Execution System (MES) serves as the critical link between enterprise-level planning and real-time shop floor operations. It provides the necessary visibility, control, and optimization to improve efficiency, reduce waste, and drive profitability.
This white paper explores how MES works, its key functionalities, and why it is essential for manufacturers striving for operational excellence and digital transformation.
What is an MES?
A Manufacturing Execution System (MES) is a software solution designed to track, monitor, and optimize manufacturing operations in real time. It connects various production processes, equipment, and business systems, providing a single source of truth for manufacturing data.
Key Functions of MES:
- Production Monitoring: Real-time tracking of machines, operators, and processes.
- Scheduling & Planning: Dynamic scheduling based on resource availability and demand.
- Quality Management: Automated quality checks and traceability for compliance.
- Maintenance Management: Predictive maintenance to reduce unplanned downtime.
- Data Integration: Seamless connection with ERP, IoT, and other enterprise systems.
How MES Works
MES acts as the digital nerve center of a manufacturing facility, collecting and processing real-time data from machines, sensors, and operators. The system provides actionable insights to optimize production efficiency and reduce operational inefficiencies.
Step-by-Step MES Workflow:
- Data Collection & Integration: MES gathers real-time data from machines, IoT devices, and human inputs.
- Production Execution & Tracking: The system tracks work-in-progress (WIP), ensuring each process aligns with planned production schedules.
- Quality Control & Compliance: MES enforces quality parameters and records production data for audits.
- Performance Analytics & Optimization: The system generates reports, KPIs, and dashboards to support continuous improvement initiatives.
- Predictive Maintenance & Downtime Reduction: MES integrates with IoT sensors to anticipate failures and optimize maintenance schedules.
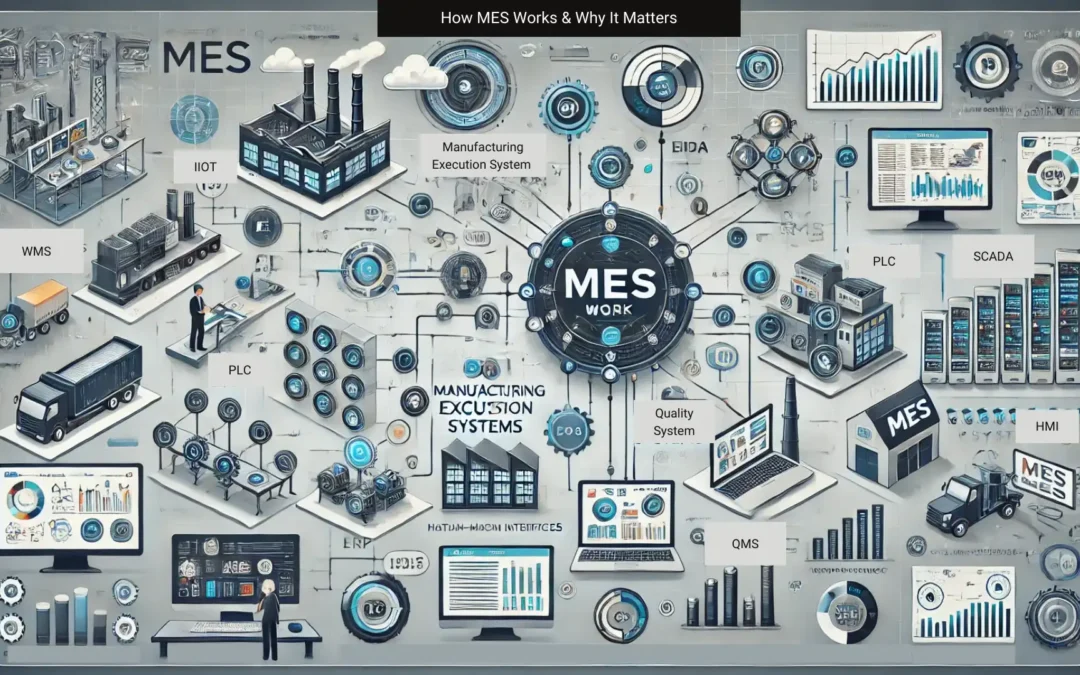
What Connects to MES & How?
MES serves as the central hub for various data sources and systems within a manufacturing environment. By integrating these components, MES enables seamless data flow and comprehensive process control.
Primary Data Sources That Connect to MES:
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Systems – Aligns business planning with production execution, ensuring accurate order fulfillment and inventory management.
- Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) Systems – Provides real-time process data from sensors and controllers to MES for monitoring and optimization.
- Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) – Transmits machine data to MES for tracking performance and automation control.
- Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) Sensors – Captures environmental conditions, equipment health, and operational efficiency metrics.
- Quality Management Systems (QMS) – Ensures production meets required quality standards by integrating with MES for real-time defect detection and compliance tracking.
- Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) – Synchronizes material movements, inventory levels, and logistics with MES to optimize production planning.
- Human-Machine Interfaces (HMIs) – Facilitates operator interactions with MES for status updates, troubleshooting, and workflow adjustments.
How MES Integrates These Data Sources:
- Data Standardization: MES converts raw data from various sources into a unified format for analysis.
- Automated Workflows: MES triggers actions based on real-time data, such as scheduling maintenance when IoT sensors detect machine anomalies.
- Real-Time Dashboards: Aggregates and visualizes data for operators and management to make informed decisions.
- Bi-Directional Communication: MES not only receives data but also sends instructions to machines, controllers, and other systems for automated execution.
Why MES Matters
Manufacturers leveraging MES experience significant improvements in efficiency, quality, and cost savings. Here’s why MES is crucial for modern manufacturing operations:
- Eliminates Data Silos
- MES unifies disparate production systems, ensuring seamless data flow across departments.
- Eliminates manual data entry and the risk of inconsistent or outdated information.
- Boosts Production Efficiency
- Reduces cycle times by automating production workflows.
- Optimizes resource utilization and minimizes bottlenecks.
- Enhances Product Quality & Compliance
- Ensures real-time quality control, reducing defects and waste.
- Provides full traceability for regulatory compliance and audits.
- Reduces Downtime & Maintenance Costs
- Predictive analytics identify potential machine failures before they occur.
- Helps prevent costly unplanned stoppages, increasing overall equipment effectiveness (OEE).
- Improves Decision-Making with Real-Time Insights
- Provides dashboards with live production data, allowing managers to make data-driven decisions.
- Enables agile responses to demand fluctuations and supply chain disruptions.
Conclusion: MES as the Foundation of Smart Manufacturing
MES is the backbone of modern manufacturing, providing the real-time data and automation needed to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and maintain quality standards. By connecting the shop floor to enterprise systems, MES enables manufacturers to achieve full visibility, control, and optimization of their operations.
Are you ready to streamline your manufacturing processes and boost efficiency with MES?
Contact a Smart Manufacturing expert to start your MES journey today.
How? : Schedule a meeting with us, and let’s talk. Click here to schedule now!